Examples#
Calculator#
It’s easy to create a good-looking program with Edifice. In this example, we imitate the look of the MacOS Calculator app in 100 lines of code (most of which is implementing the calculator state machine).
Source code calculator.py.
python examples/calculator.py
python -m edifice --inspect examples/calculator.py Main
Financial Charting#
In this example, we create a reactive charting application with Edifice which fetches stock data from Yahoo Finance.
Source code financial_charts.py.
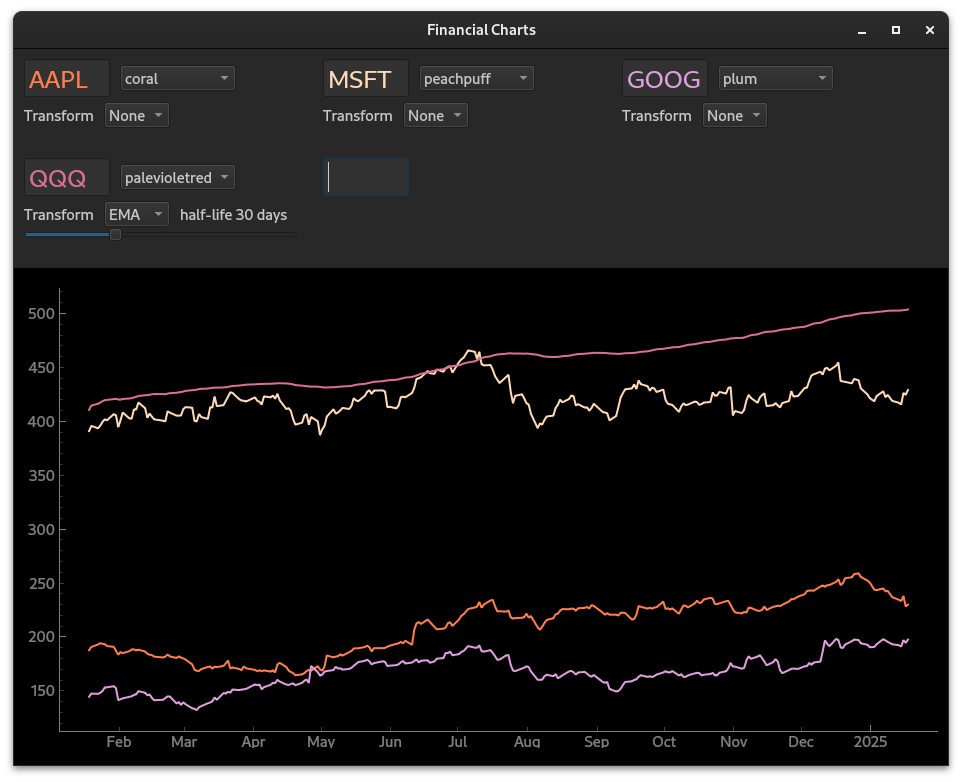
python examples/financial_charts.py
python -m edifice --inspect examples/financial_charts.py Main
TodoMVC#
An implementation of TodoMVC in Edifice.
TodoMVC is a simple todo list program written in many JavaScript frameworks, so that web developers can compare the frameworks by comparing the TodoMVC implementations.
For comparison, see the Edifice TodoMVC source code todomvc.py.
python examples/todomvc.py
python -m edifice --inspect examples/todomvc.py Main
Harmonic Oscillator#
An example of animation in Edifice.
Source code harmonic_oscillator.py.
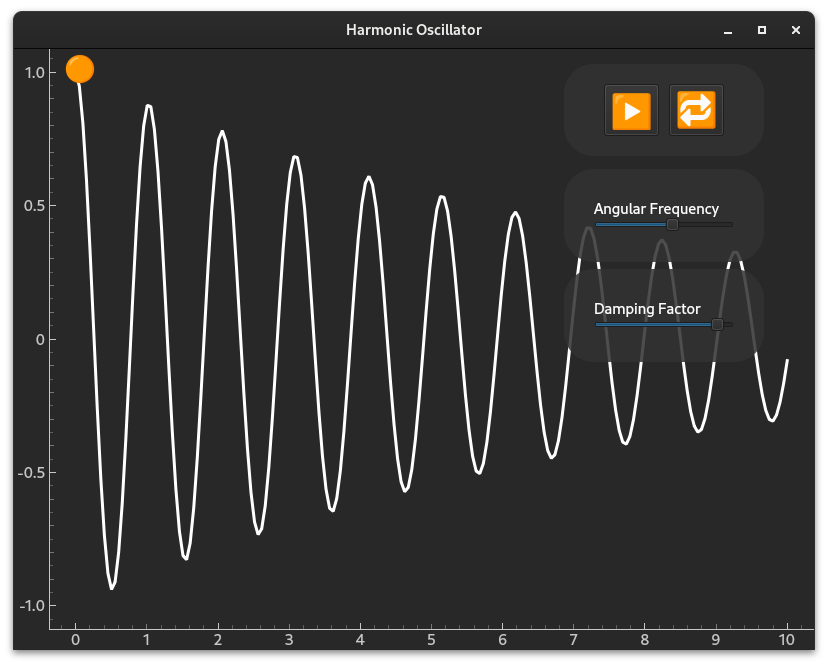
python examples/harmonic_oscillator.py
python -m edifice --inspect examples/harmonic_oscillator.py Main
7GUIs Tasks#
These examples implement The 7 Tasks in Edifice for 7Guis: A GUI Programming Benchmark
Counter#
Counter serves as a gentle introduction to the basics of the language, paradigm and toolkit for one of the simplest GUI applications imaginable.

Source code 7guis_01_counter.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_01_counter.py
Temperature Converter#
Temperature Converter increases the complexity of Counter by having bidirectional data flow between the Celsius and Fahrenheit inputs and the need to check the user input for validity.
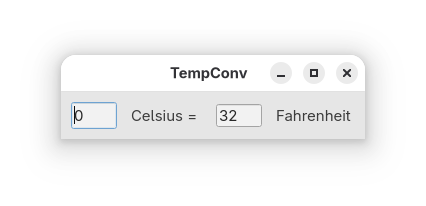
Source code 7guis_02_temperature_converter.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_02_temperature_converter.py
Flight Booker#
The focus of Flight Booker lies on modelling constraints between widgets on the one hand and modelling constraints within a widget on the other hand.
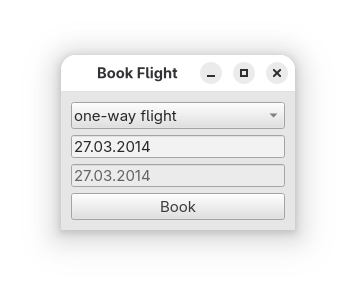
Source code 7guis_03_flight_booker.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_03_flight_booker.py
Timer#
Timer deals with concurrency in the sense that a timer process that updates the elapsed time runs concurrently to the user’s interactions with the GUI application.
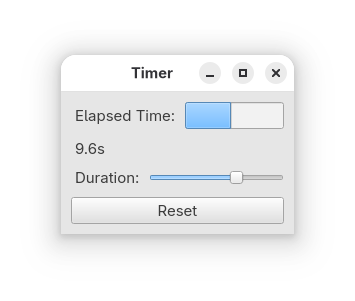
Source code 7guis_04_timer.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_04_timer.py
CRUD#
CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) represents a typical graphical business application.
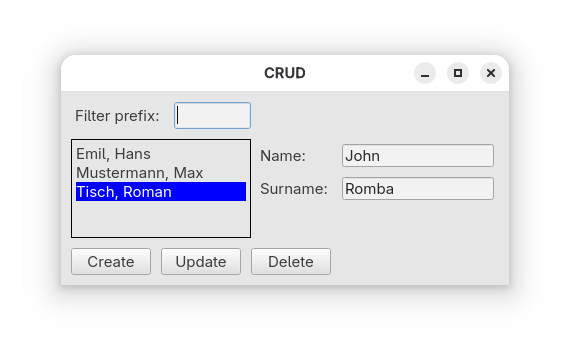
Source code 7guis_05_crud.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_05_crud.py
Circle Drawer#
Circle Drawer ’s goal is, among other things, to test how good the common challenge of implementing an undo/redo functionality for a GUI application can be solved.
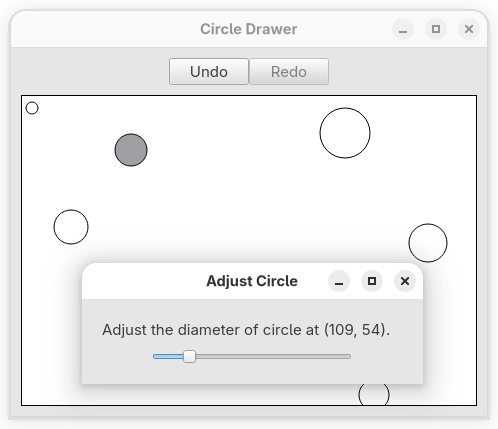
Source code 7guis_06_circle_drawer.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_06_circle_drawer.py
Cells#
Cells is a more authentic and involved task that tests if a particular approach also scales to a somewhat bigger application. The two primary GUI-related challenges are intelligent propagation of changes and widget customization.
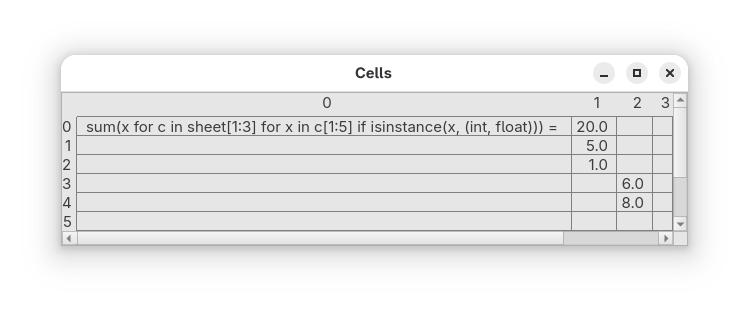
Source code 7guis_07_cells.py
python examples/7guis/7guis_07_cells.py
This is a modified implementation of Cells.
The spreadsheet is 10×10 instead of 100×100.
We can use the Qt supported HTML subset to markup text in the cells.
Cells Formulas#
I didn’t feel like implementing the whole SCells spreadsheet formula language so instead the spreadsheet formula language is Python.
If a cell begins with an equals sign = then it is parsed as a formula expression.
The formula expression following = will be passed to Python
eval
with one variable in scope: sheet.
sheet:tuple[tuple[int | float | str, ...], ...]
The formula expression can use the sheet variable to access the other cells
in the spreadsheet.
The sheet variable is the spreadsheet as a tuple of tuples.
It is column-major order, and the indices are 0-based.
The formula expression must evaluate to int, float, or str.
Python filtered list comprehensions are good for writing formulas. The Common Sequence Operations also supply a lot of the features of a spreadsheet formula language.
=sheet[5][6]
=sum(x for x in sheet[0] if isinstance(x, (int, float)))
=",".join(col[0] for col in sheet if isinstance(col[0], str))
=max(x for c in sheet[:3] for x in c[:5] if isinstance(x, (int, float)))
=sum(x for c in sheet[1:3] for x in c[1:5] if isinstance(x, (int, float)))